You should know the main NdFeB magnet grades for 2025. The most common grades are N35, N42, N50, and N52. Each grade changes how strong, expensive, or useful the magnet is. When you pick magnets, think about these things:
-
Higher grades give stronger magnet power.
-
Heat or cold can change magnet strength.
-
The way a magnet is magnetized changes how you use it.
-
The size and shape of the magnet are important for your project.
-
Coatings help stop magnets from rusting.
-
Try to find a good balance between price and how well the magnet works.
-
Ask someone who knows more if you are not sure.
-
Make sure the magnets follow the rules for the environment.
NdFeB Magnet Grades Overview
Grades of Neodymium Magnets
There are many grades of neodymium magnets. These grades show how strong the magnet is. They also show how it works in different places. Grades use numbers and letters for their specification. The number tells you how strong the magnet is. The letter shows how much heat the magnet can take. For example, N38 and 40SH are common grades. Look at the table below to compare them:
|
Grade |
Series |
Max Operating Temperature |
Magnetic Energy (BH) Max |
|---|---|---|---|
|
N38 |
N |
≤ 80 ℃ |
36-39 MGOe |
|
40SH |
SH |
≤ 150 ℃ |
38-41 MGOe |
Higher numbers mean the magnet is stronger. The letter, like SH, means it can handle more heat. Grades like N42 and N52 are very strong. Use these grades when you need powerful magnets. Neodymium magnets are the strongest permanent magnets. They are made from neodymium-iron-boron alloy. Always check the grade and specification before you pick a magnet.
Why Magnet Grades Matter
Magnet grades are important for how your magnet works. Different grades change the strength, heat resistance, and price. If you choose the wrong grade, your magnet may not work well. It might not last long. Here are some reasons why grades matter:
-
NdFeB magnet grades give strong and useful magnets for many jobs.
-
Grades change how much force the magnet has. They also change how hot it can get before it gets weak.
-
Picking the right grade helps your magnet last longer and work better.
N42 magnets are used in electronics like speakers and hard drives. Higher grades like N48 or N52 are best for motors and wind turbines. Medical devices need high grades for power and accuracy. Always match the grade to what you need. Check the specification to get the best magnet for your project.
Understanding NdFeB Magnet Grade Codes
Grade Numbers Explained (N30-N55)
You see grade numbers like N30, N42, or N52 on neodymium magnets. These numbers show you how strong the magnet is. The number stands for the maximum energy product, measured in Mega-Gauss Oersteds (MGOe). A higher number means a stronger magnet. For example, N30 is stronger than lower grades like N24. N50 is one of the highest grades you can find easily. N52 is even stronger, but you only get it in certain sizes. When you choose a magnet, look at the grade number first. It helps you know if the magnet will work for your project.
Grade Letters and Their Meaning
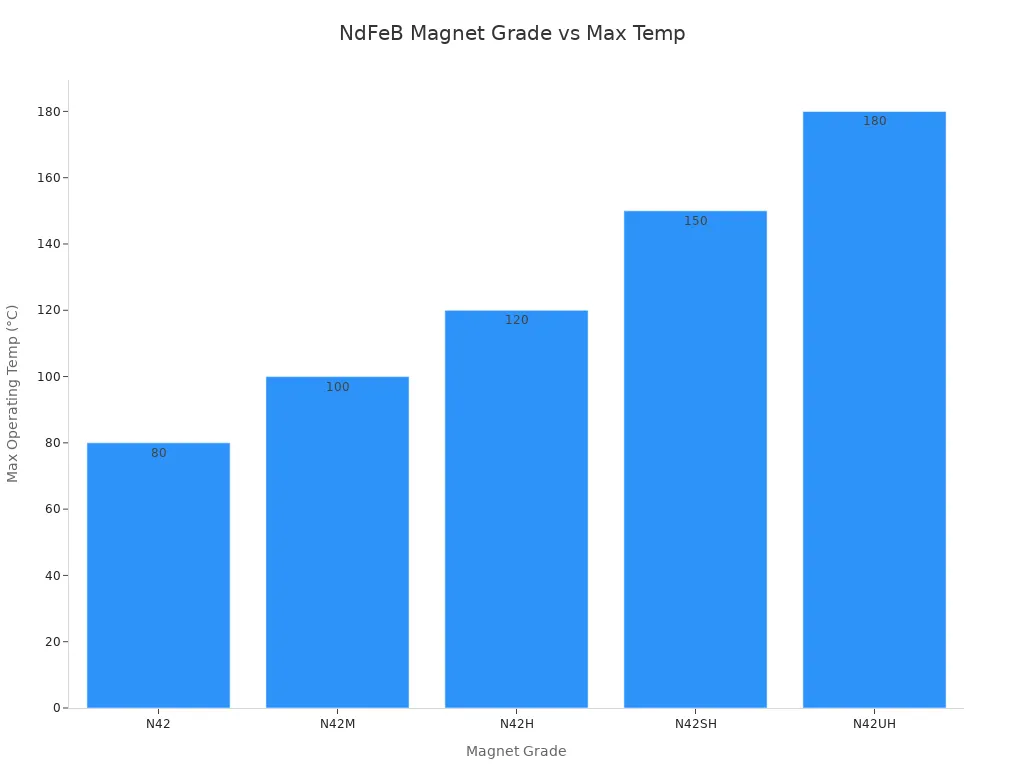
After the number, you often see a letter, such as N42SH or N52H. This letter tells you how much heat the magnet can handle before it loses strength. The letters M, H, SH, and UH show increasing temperature resistance. Higher letters mean the magnet works at higher temperatures. For example, N45M can work up to 100°C. You need to check the letter if your magnet will be in a hot place.
|
Grade |
Maximum Operating Temperature |
|---|---|
|
N42 |
~80 °C |
|
N42M |
~100 °C |
|
N42H |
~120 °C |
|
N42SH |
~150 °C |
|
N42UH |
~180 °C |
What Magnet Grades Indicate
Magnet grades tell you more than just strength and temperature. You also learn about other important properties. Here are some things you should know:
-
Remanence (Br): Shows how much magnetism stays after you magnetize the magnet.
-
Coercivity (Hcb): Tells you how well the magnet resists losing its magnetism.
-
Intrinsic Coercivity (Hcj): Shows how well the magnet keeps its strength, even at high temperatures.
-
Maximum Energy Product (BHmax): Tells you how much energy the magnet can store.
-
Operating Temperature: Shows the highest temperature the magnet can work at without losing power.
You should always check these properties when you pick a magnet. If you need a magnet for a hot place, choose a grade with a higher letter. If you need a strong magnet, pick a higher number. This helps you get the best magnet for your needs.
Popular NdFeB Magnet Grades in 2025
Magnetic Strength Comparison
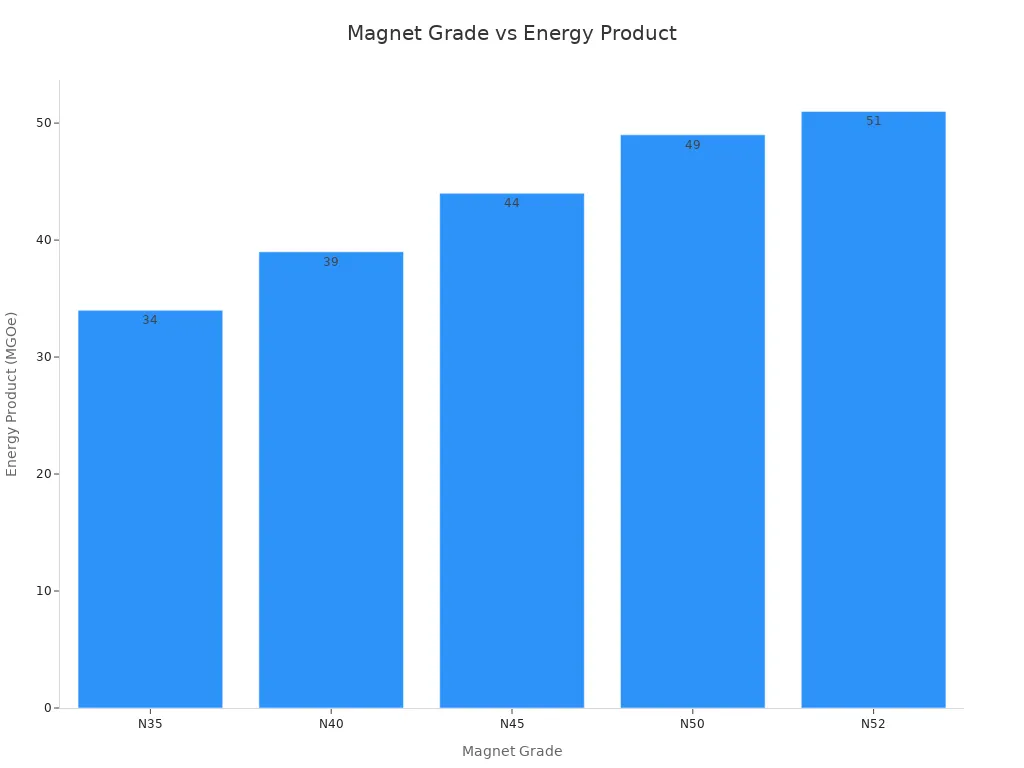
Magnetic strength is very important when picking neodymium magnets. The most used grades are N35, N40, N45, N50, and N52. Each grade gives a different amount of power. If you want a strong magnet, look at the energy product. This number shows how much magnetic energy the magnet can hold.
Here is a table that lists the energy product for each grade:
|
Magnet Grade |
Energy Product (MGOe) |
|---|---|
|
N35 |
33-35 |
|
N40 |
38-40 |
|
N45 |
42-46 |
|
N50 |
47-51 |
|
N52 |
49-53 |
N52 NdFeB magnet is the strongest grade in this group. N35 is the weakest of these grades. If you want more strength, pick a higher grade. Stronger magnets usually cost more money. You need to think about both power and price.
Temperature Resistance
Heat can change how well neodymium magnets work. If you use a magnet in a hot place, check its grade. Most common grades work up to 90°C (194°F). If you use a magnet above this, it might lose power.
|
Magnet Grade |
Maximum Operating Temperature |
|---|---|
|
NdFeB Group |
90°C / 194°F |
Some grades have letters like H or SH. These can work at higher temperatures. Always check the grade before using a magnet in heat. If you pick the wrong one, it might get weak or stop working.
Tip: Make sure the grade matches the temperature where you use it. This helps your magnets last longer and work better.
Common Applications
Neodymium magnets are used in many things. The car industry uses the most NdFeB magnet grades, especially for electric vehicles. These magnets help motors run well and save energy. You also find them in electronics, wind turbines, and medical tools.
Here are some common uses for permanent magnets:
-
Electric motors in cars and bikes
-
Wind turbines for clean energy
-
Hard drives and speakers in electronics
-
MRI machines and medical tools
Asia-Pacific makes and uses the most neodymium magnets. China makes most of the magnets you see today. Modern sintered NdFeB magnets are the most used, with about 58.1% of the market in 2024. These magnets are strong and work well in many products.
Sintered vs. Bonded NdFeB Magnets
You can pick sintered or bonded neodymium magnets. Sintered magnets are made by pressing and heating the material. These magnets are stronger and work better. Bonded magnets are made by mixing powder with resin or plastic. These are easier to shape and lighter, but not as strong.
If you need strong magnets for motors or turbines, pick sintered grades. If you need magnets for sensors or small devices, bonded grades may be better. Think about what you need and choose the right type.
Note: Sintered NdFeB magnets are the top choice for high-performance uses in 2025.
Always check the grade and type before buying neodymium magnets. This helps you get the best magnet for your needs.
Choosing the Right Neodymium Magnet Grade
Matching Magnet Grades to Application
You need to pick the right magnet grade for your job. Every magnet works best in certain places. Before you choose, think about what you want the magnet to do. Some neodymium magnets are good for motors. Others work better in sensors or speakers. Always check the magnet’s details before you buy.
Here are steps to help you choose the right grade:
-
Write down what you need for your project. Think about the size, shape, and strength you want.
-
Look at the grades you can pick from. Higher grades are stronger. Lower grades cost less but might not work for everything.
-
See if your project needs the magnet to work in heat. Some grades lose power when they get hot.
-
Ask if the magnet will face strong outside forces. If yes, pick a grade that resists losing its magnetism.
-
Check the table below to see which grades fit common uses:
|
Application |
Recommended Grade |
Reason |
|---|---|---|
|
Electric Motors |
N48, N52 |
Needs strong magnets |
|
Sensors |
N35, N40 |
Needs medium strength |
|
Wind Turbines |
N50, N52 |
Needs strong and steady |
|
Speakers |
N42, N45 |
Needs good sound |
|
Medical Devices |
N52 |
Needs power and accuracy |
Tip: Always pick the magnet grade that matches your project for the best results.
Environmental and Safety Factors
You need to think about the environment and safety when picking magnets. Some magnets work better in wet places. Others need coatings to stop rust. If your project faces water or chemicals, pick a magnet with a protective layer.
Safety is important too. Strong magnets can hurt fingers or mess up electronics. Handle them carefully. If magnets are used near people, pick grades that are safe and easy to control.
Think about these things for safety and the environment:
-
Will the magnet touch water or chemicals? Use coated magnets.
-
Does your project need magnets to work in heat? Pick grades with letters like H or SH.
-
Are magnets used near sensitive devices? Pick grades with steady magnetic fields.
-
Do you need to follow rules for the environment? Make sure your magnets meet local standards.
Note: Picking the right magnet keeps your project safe and helps magnets last longer.
Cost and Performance Balance
You want to find a good balance between cost and power. High grades give more power, but cost more. Lower grades save money, but might not work for every job.
Here’s how to find the best balance:
-
Write down what your project needs. Decide if you need strong magnets or just basic strength.
-
Compare prices for different grades. Sometimes a middle grade works well and saves money.
-
Think about how long you want the magnet to last. Stronger magnets last longer in tough jobs.
-
If your project faces heat or strong forces, buy a better grade.
-
Use the table below to compare cost and strength:
|
Grade |
Strength |
Cost |
Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
N35 |
Low |
Low |
Simple jobs |
|
N42 |
Medium |
Medium |
Electronics, speakers |
|
N50 |
High |
High |
Motors, turbines |
|
N52 |
Highest |
Highest |
Medical, precise jobs |
Picking the right magnet grade helps you get the best value for your project.
Always check the magnet’s details before you buy. This helps you pick the right grade for your project, environment, and budget. Good magnet choice makes your project work better and last longer.
New Trends in NdFeB Magnet Grades
Recent Innovations
There are many new things happening with magnets. Companies now use better ways to make neodymium magnets stronger. These new methods also make magnets last longer. Recycling old magnets is easier now. This saves materials and helps lower costs. Some companies try to make magnets without rare earth elements. This helps stop supply problems and is better for the planet.
Scientists are finding ways to make magnets work better. They use special coatings to stop rust and damage. Some magnets can now handle more heat than before. This means you can use them in more places, like electric cars and wind turbines. There are also new shapes and sizes for special uses.
Tip: Look for magnets with new coatings and better heat resistance. These features help your projects last longer.
Emerging Grades for 2025
In 2025, you will see new grades of neodymium magnets. These new grades are stronger and more stable. Some magnets use less dysprosium, so they cost less and are easier to make. Sintered magnets keep getting stronger each year. Bonded magnets are lighter and easier to shape.
Here are some trends you should know:
-
The strong NdFeB magnet market is growing fast. Experts think it will reach USD 25.6 billion by 2030.
-
Electric vehicles need stronger magnets.
-
New ways to make magnets help them work better.
-
More magnets are made without rare earth metals.
-
Samarium cobalt magnets are also getting better for high-heat jobs.
|
Magnet Type |
Key Feature |
Best Use |
|---|---|---|
|
Neodymium magnets |
High strength |
Motors, electronics |
|
Sintered magnets |
Strongest type |
Wind turbines, vehicles |
|
Bonded magnets |
Easy to shape |
Sensors, small devices |
|
Samarium cobalt magnets |
Heat resistance |
Aerospace, medical |
You should watch for new grades and new technology. These changes help you choose the best magnet for your needs.
You now know how NdFeB magnet grades differ in strength, temperature resistance, and cost. When you choose a magnet, match the grade to your project’s needs. Look at both popular and new grades for 2025.
-
Check the grade number for strength.
-
Look for letters that show heat resistance.
-
Compare prices and uses.
Tip: Stay updated on magnet technology by following news from magnet suppliers and industry reports. This helps you find the best magnets for your future projects.